Cloud sourcing refers to the practice of obtaining services, infrastructure, platforms, software, and other IT resources from cloud-based providers rather than hosting solutions in-house.
It enables organizations to leverage the economies of scale, specialized expertise, and flexibility of cloud vendors. Learn more about What is Cloud Sourcing.
Table of Contents
Benefits of Cloud Sourcing
Adopting a cloud-sourcing strategy offers several key advantages:

Cost Savings
Cloud sourcing eliminates the need for upfront investments in IT infrastructure and shifts spending to a utility-based operational expense model. Organizations only pay for the services they use, leading to significant cost savings.
Speed and Agility
Cloud resources can be rapidly provisioned on-demand, providing the speed and agility to quickly test new ideas and scale services up or down as needed. This accelerates time-to-market.
Access to Specialized Skills
Cloud vendors have deep technical expertise and experience delivering and optimizing cloud-based solutions, providing access to specialized skills that would be costly to develop in-house.
What are Cloud Sourcing Models
There are three primary ways organizations leverage cloud sourcing:
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO)
With BPO, companies outsource business processes like payroll, HR, accounting, and supply chain management to a cloud services provider. This focuses internal efforts on core competencies.
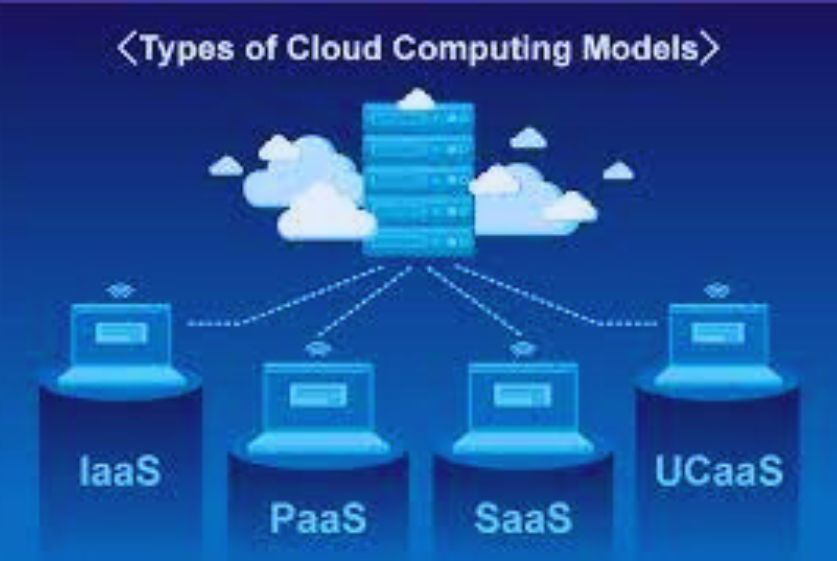
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides on-demand access to fundamental computing infrastructure resources like servers, storage, and networking over the Internet. This eliminates the need to purchase and manage physical data centers.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the cloud on a subscription basis rather than installing and maintaining them on-premises. Common examples include email, CRM, ERP, and collaboration tools.
Risks and Challenges
While cloud sourcing provides many benefits, it also comes with certain risks and implementation challenges:
Security and Compliance
Mission-critical data and workloads are transferred to external cloud providers, posing potential security and regulatory compliance risks if not properly addressed.
Loss of Control
Organizations cede a certain degree of direct control over resources and systems to the cloud vendor, which requires trust and partnership.
Vendor Lock-in
Lack of interoperability and proprietary technologies can make it difficult to switch cloud vendors, creating vendor lock-in. Carefully avoiding this is key.
Best Practices for Implementation
Follow these best practices to successfully adopt cloud sourcing:
Clearly Define Requirements
Document detailed technical, security, compliance, performance, and availability requirements to evaluate vendors objectively.

Maintain Open Communication
Facilitate continuous open communication between your team and vendor to drive transparency and quickly resolve any issues.
Start Small and Scale Up
Begin with a limited pilot to validate capabilities before scaling usage more broadly across the organization. Take an iterative approach.
Conclusion
Cloud sourcing leverages specialized cloud vendors to provide services, platforms, infrastructure, and software through scalable on-demand models. While it can drive significant benefits like cost savings and agility, careful planning is required to manage risks and implementation challenges.
Following best practices like clearly defining needs, maintaining open vendor communication, and taking a phased approach enables organizations to successfully tap into the full potential of cloud sourcing.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of cloud sourcing?
The main benefits are cost savings, increased speed and agility, and access to specialized skills and expertise.
What are some common cloud-sourcing models?
Common models include IaaS for infrastructure, SaaS for software/apps, and BPO for business process outsourcing.
What risks should be evaluated before adopting cloud sourcing?
Key risks to evaluate are security, compliance, loss of control, and vendor lock-in.
How can organizations avoid vendor lock-in with cloud sourcing?
Avoiding proprietary technologies, insisting on data portability, and using multiple vendors can help avoid lock-in.
What is the best way to start implementing cloud sourcing?
Beginning with a limited pilot or proof of concept and slowly scaling up adoption is the best way to start.