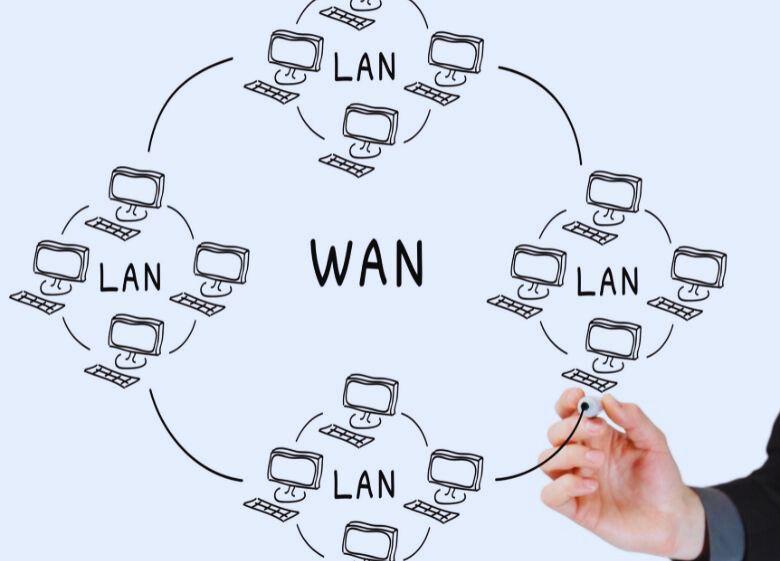
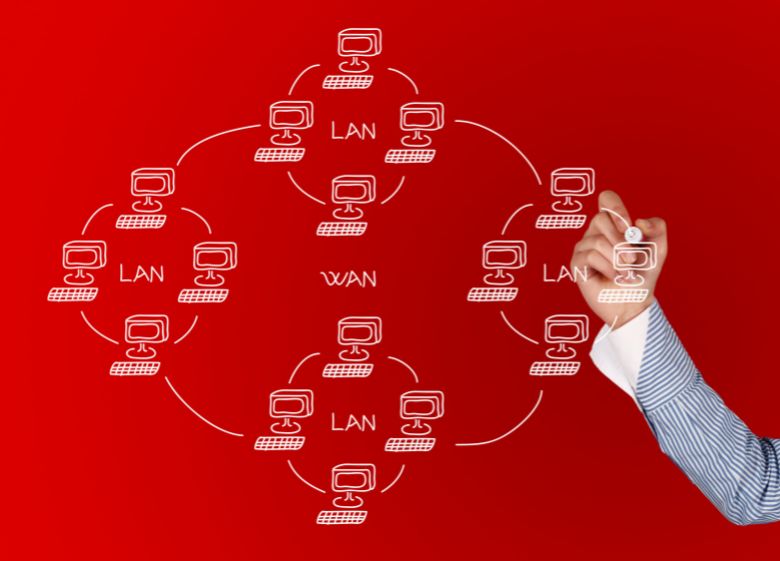
A WAN network diagram visually depicts the layout and connections between sites in a geographically dispersed network. WAN (wide area network) diagrams are important for designing, documenting, and troubleshooting enterprise networks.
This guide will cover the basics of what a WAN is, the components of a WAN diagram, types of WAN diagrams, how to create a WAN diagram, and tips for clear and effective WAN network diagrams.
Table of Contents
What is a WAN?
A WAN connects LANs (local area networks) and other networks over long distances. Unlike a LAN which is contained within a small geographical area like an office or building, a WAN can span entire cities, states, or countries.
WANs use dedicated, high-capacity connections like MPLS and VPN tunnels to securely connect geographically dispersed sites. This allows remote branch offices to access resources at a central corporate network or data center. Traffic and data are efficiently routed between sites on the WAN.
Components of a WAN
A WAN diagram will include symbols representing the various devices that make up the WAN architecture:
- Routers: Connect LANs and WANs and route traffic between them. Routers interconnect multiple networks.
- Switches: Connect devices within a LAN and segment traffic.
- Firewalls: Provide security and control access between the WAN and connected networks. Firewalls protect traffic entering or leaving the WAN.
- Connections: The specific WAN links between sites and locations. Popular options include MPLS, VPN tunnels, leased lines, and Internet-based connections.
Types of WAN Network Diagram
There are two main types of WAN diagrams, logical and physical.
Logical WAN Diagram
A logical diagram focuses on the network topology, showing how different sites connect through the WAN, without specifying the physical components. Logical diagrams provide a high-level overview of the WAN architecture.
Physical WAN Diagram
A physical WAN diagram displays the actual devices and connections in the network. It maps out the routers, switches, firewalls, and wiring or circuits that link sites. Physical diagrams are more complex but show the tangible hardware making up the WAN.
Steps to Create a WAN Diagram
Follow these steps to diagram a new or existing WAN:
Determine Network Requirements
First gather information on the number of locations, bandwidth needs, security policies, and applications for the WAN. This determines diagram components.
Map Out Locations
Plot each location that will connect to the WAN. Note its geographic placement and relationship to other sites.
Add WAN Devices
Insert shapes to represent key WAN hardware like routers, switches, and firewalls.
Connect Devices
Draw lines linking WAN devices to show the flow of data between them.
Specify Connections
Label the connections between sites with details like VPN or MPLS.
Tips for WAN Diagrams

Keep it Simple
Focus on important details and avoid cluttering the diagram.
Use Standard Symbols
Use accepted icons and shapes for network devices and topology.
List Components
Provide a legend detailing the devices and connections used.
Include Labels
Label sites, devices, and connections for easy understanding. A WAN network diagram provides an at-a-glance view of the topology and components that make up a geographically dispersed network.
Both logical and physical diagrams are important for planning and managing enterprise WANs. Following the diagram best practices ensures efficient and effective WAN documentation.
FAQs
What is the difference between LAN and WAN?
A LAN is localized within a small area like a building, while a WAN connects LANs and other networks across a large geographic area. LANs use Ethernet and WANs use dedicated connections like MPLS or VPNs.
What are the most important elements to include in a WAN diagram?
The key elements are the various locations/sites, WAN devices like routers and firewalls, and the labeled connections between sites.
What software tools can be used to create WAN diagrams?
Popular options include Microsoft Visio, Lucid Chart, Cisco Network Topology Mapper, and Netrin. These provide drag-and-drop tools for network diagramming.
Should I create a logical or physical WAN diagram?
It’s best to have both a logical diagram showing the topology and a physical diagram displaying the hardware components. Together they provide a comprehensive overview of the WAN.
What common symbols and icons are used in WAN diagrams?
Standard symbols include rectangles/clouds for sites, circles/ovals for routers, diamonds for switches, triangles for firewalls, and lines or arrows for connections.