Cloud Computing Index refers to the delivery of computing services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the Internet. With cloud computing, companies can access technology services on demand, without having to build and maintain expensive computing infrastructure.
Cloud computing provides a simple way to access servers, storage, databases, and a broad set of application services over the Internet.
A defining characteristic of cloud computing is that the computing infrastructure is operated solely by a cloud services provider like Google, Amazon or Microsoft.
Table of Contents
The Rise of Cloud Computing
Though the term “cloud computing” began gaining popularity in the late 2000s, the roots of cloud computing trace back to the 1950s when large-scale mainframes were made available to schools and corporations.
These mainframes functioned as an early form of cloud computing, allowing multiple users to access computing power from their terminals.
The launch of Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2006 marked a major evolution in cloud computing. AWS provides a suite of cloud-based services, including computing power, storage, and databases, available on demand through the Internet. This allowed companies to launch and scale applications quickly without having to build their computing infrastructure.
Since 2006, cloud computing has exploded in popularity and use with businesses large and small turning to platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform to power their applications, websites, storage, and more.
Today, cloud computing is a multibillion-dollar industry and an indispensable foundation for companies operating online.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing Index
Several key characteristics of cloud computing distinguish it from traditional on-premises IT environments:

- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision computing capabilities like server time and network storage automatically as needed without requiring human interaction with a service provider.
- Broad Network Access: Services are delivered over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms on a variety of devices (laptops, tablets, smartphones).
- Resource Pooling: Computing resources are pooled to serve multiple users through a multi-tenant model with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to user demand.
- Rapid Elasticity: Capabilities can be elastically provisioned to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the service appears to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
- Measured Service: Usage of cloud resources can be monitored, controlled, and reported providing transparency for both the provider and consumer. Usage is typically billed on a utility or consumption basis.
Cloud Computing Services Models
There are three fundamental cloud computing service models:
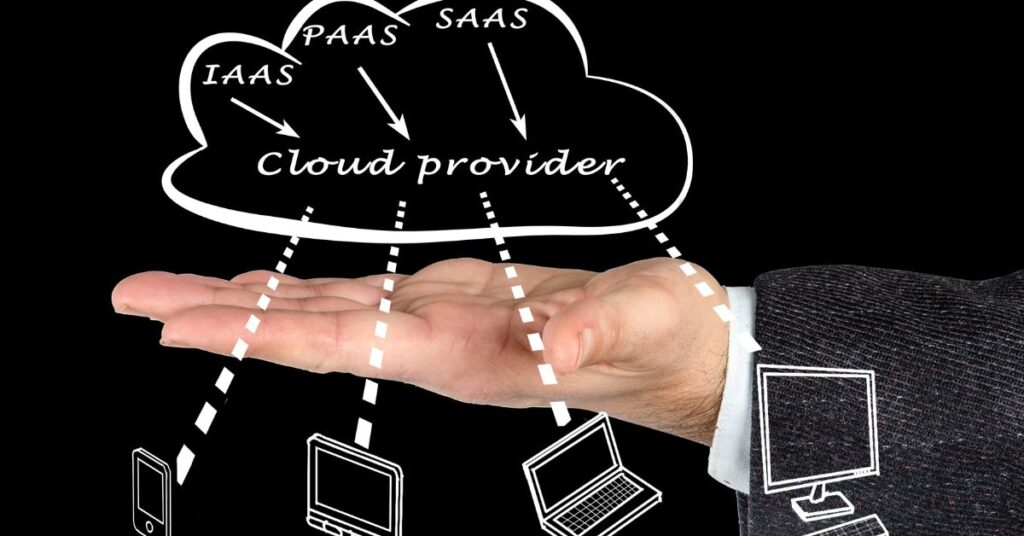
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): The basic building blocks of computing are provided as a service over the internet i.e. servers, storage, and networking. This allows businesses to avoid purchasing and managing physical servers themselves. AWS EC2 and Google Compute Engine are examples of IaaS.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): A ready-to-use development environment and API suite is provided to developers to build cloud-based applications. Google App Engine and AWS Elastic Beanstalk are examples of PaaS.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS): Completed cloud-based application software is delivered on demand over the internet, eliminating the need for businesses to install and run applications on their systems. Examples include Gmail, Slack, and Salesforce.
Cloud Deployment Models
There are also key cloud deployment models:
- Public Cloud: Cloud infrastructure and services are provisioned for open use by the general public over the Internet. Public cloud providers include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
- Private Cloud: Cloud infrastructure is provisioned for use by a single organization comprised of multiple users. Resources are managed on-premise or provisioned on third-party infrastructure exclusively for the organization.
- Hybrid Cloud: Public and private cloud models are bound together to enable data and application portability. Businesses can take advantage of the scalability of the public cloud along with the control of the private cloud.
Top Cloud Computing Providers
The top cloud computing providers today include:

- Amazon Web Services (AWS): The largest public cloud provider with a wide range of IaaS and PaaS services including EC2, S3, and Lambda.
- Microsoft Azure: A rapidly growing public cloud platform with services ranging from computing, databases, analytics, networking, and more.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Provides a suite of public cloud computing services including computing, data storage, data analytics, and machine learning.
- IBM Cloud: Offers an array of cloud computing services with a focus on enterprise needs including AI, Internet of Things, blockchain, and quantum computing.
- Oracle Cloud: Provides SaaS applications, platform services, and infrastructure services via Oracle’s global network of managed cloud regions.
- Alibaba Cloud: The largest public cloud provider in China providing a complete suite of global cloud computing services.
Cloud Computing Use Cases
Some common use cases that cloud computing enables:
- Run compute-intensive applications like AI, machine learning, and high-performance computing.
- Deliver highly scalable web applications that can handle traffic spikes.
- Store and backup large amounts of data at a low cost.
- Host databases to power dynamic web applications and sites.
- Stream media and video content globally to large concurrent audiences.
- Develop and test applications faster.
- Deploy production applications and updates quickly.
- Leverage serverless computing to focus on code vs infrastructure.
Cloud Computing Architecture
The cloud computing architecture consists of:
- A front-end platform (laptops, tablets, phones) that customers use to access the cloud.
- A back end of hardware and software resources that create the cloud services (servers, storage, networking, orchestration).
- A cloud-based delivery model to provision resources on-demand.
- The internet is the connectivity medium between front-end platforms and back-end cloud resources.
Cloud Computing Security Concerns
While cloud computing provides many benefits, some security concerns include:
- Potential unauthorized exposure of sensitive data.
- Loss of governance and control over data.
- Multi-tenancy risks from resource sharing.
- Unknown overall risk profile of the cloud provider’s infrastructure.
- Dependency on the cloud provider for security.
- Compliance challenges facing regulatory and internal requirements.
The Business Benefits of Cloud Computing
Adopting cloud computing provides businesses with many benefits:
- Agility – provision resources as you need them to scale rapidly
- Cost Savings – no upfront infrastructure investments
- Flexibility – use resources on-demand to meet changing needs
- Productivity – deploy resources faster so developers can focus on code
- Performance – leverage high-performance computing on demand
- Reliability – take advantage of cloud provider expertise in resilience
- Scalability – scale up and down to meet fluctuations in demand
The Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing will continue to expand in adoption and importance with businesses. Other key trends include:
- Growth in enterprise implementation of hybrid and multi-cloud systems.
- More mission-critical workloads like analytics moving to the cloud.
- Expanding services around AI, IoT, blockchain, quantum, and edge computing.
- Simplified development and management of cloud-based applications.
- Increased regulatory clarity and compliance for cloud security and data control.
Conclusion
Cloud computing delivers scalable and flexible computing resources as a service over the internet. It enables businesses to launch applications faster, lower costs, and drive productivity without managing complex IT infrastructure.
Cloud computing has evolved from early mainframe days to mass adoption today with public providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure. Security, governance, and compliance remain key concerns.
However, the growth opportunities are vast as more enterprise workloads transition to the cloud’s benefits. Cloud computing will only increase in importance as a critical foundation for business computing.
FAQs
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of computing services like servers, databases, storage, applications, networking, and intelligence over the internet. Companies can tap into these resources without managing on-premises infrastructure.
What are the benefits of cloud computing?
Benefits include flexibility, scalability, cost savings, rapid deployment, productivity, performance, reliability, and security. Companies can provision exactly the resources their application needs.
What are the different cloud computing models?
There are public, private, and hybrid cloud models. The public cloud makes resources openly available. A private cloud is for a single organization’s internal use. Hybrid combines public and private models.
Is cloud computing secure?
Major public cloud providers offer robust security tools, practices, and expertise. However, organizations are still responsible for their data, access, and compliance. Proper cloud security measures are essential.
What does the future hold for cloud computing?
The cloud computing market will continue rapid growth as more enterprise workloads transition to the cloud for its benefits and new services emerge in areas like AI, blockchain, quantum, and edge computing.









