Cloud computing has transformed business operations over the past decade. By utilizing on-demand, internet-based information technology (IT) services, businesses can reduce costs, scale rapidly, and enable remote work. This article examines the key benefits business value of cloud computing delivers for enterprises and why it has become an essential digital platform.
Table of Contents
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the on-demand delivery of IT resources, applications, and services over the Internet. Rather than maintaining data centers and servers, businesses can leverage the cloud to access technology services without needing complex on-site infrastructure. Resources are delivered quickly and flexibly via the cloud on a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
There are three main cloud computing models:
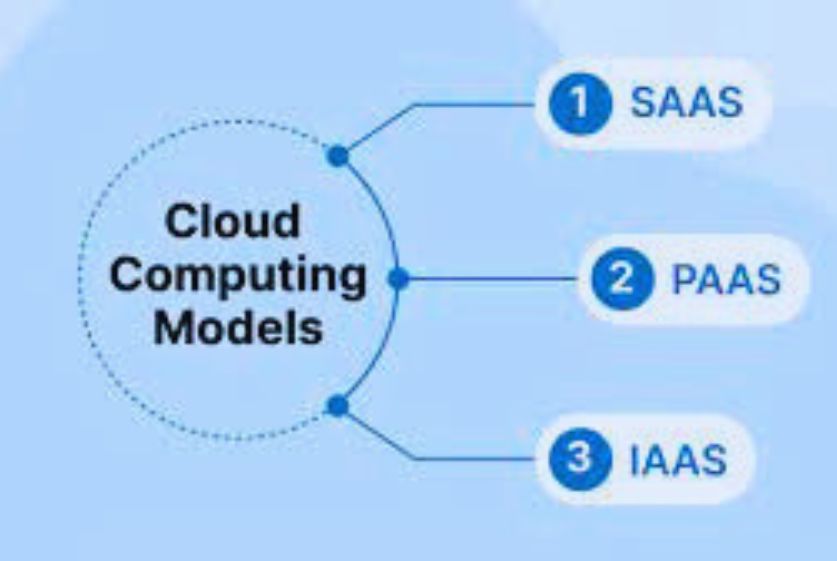
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS offers essential cloud infrastructure components such as servers, networking, storage, and data centers as an on-demand service. It provides the foundation for all cloud services.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a cloud platform for customers to develop, manage, and deliver applications without building the underlying infrastructure. It facilitates rapid software development and deployment.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS allows users to access cloud-hosted software applications over the internet. Common examples include email, collaboration tools, customer relationship management (CRM), and enterprise resource planning (ERP).
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Adopting cloud services offers significant strategic and economic benefits, including:
Cost Savings
Cloud computing eliminates high upfront capital expenditures on hardware and data centers for enterprises. The pay-as-you-go subscription model converts fixed costs into variable costs, meaning businesses only pay for the resources they use.

Scalability
Cloud platforms allow businesses to scale services up and down on demand when needs fluctuate, adding or reducing capacity rapidly. This agility is vital for modern, digital business operations.
Flexibility
The on-demand nature of cloud computing brings immense flexibility. Services can be provisioned minutes after request, supporting experimentation with new technologies.
Mobility
Enabling remote network access allows employees to work productively anytime, anywhere with an internet connection. Cloud facilitates mobile working and business continuity.
Security
Leading cloud providers implement robust, enterprise-grade security practices far exceeding what most organizations can achieve on-premises. Cloud also simplifies security management and compliance.
Business Value of Cloud Computing
Beyond the operational and economic efficiencies, migrating business functions to the cloud has strategic impacts including:
Increased Productivity
By reducing time spent on IT administration and maintenance, cloud computing enables staff to focus on innovation and deliver more business value. It also facilitates collaboration.
Faster Innovation
The flexibility of cloud platforms allows enterprises to experiment rapidly with new technologies like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain to create a competitive advantage.
Improved Collaboration
Cloud-based productivity and collaboration tools break down information silos and connectivity barriers between teams and business units. This spurs innovation and faster decision-making.
Enhanced Customer Experiences
Scalable cloud platforms allow businesses to quickly develop and launch customer-focused mobile and web applications to better understand and serve consumers.
Cloud Computing Use Cases
Many business functions can benefit from cloud adoption, including:
Data Storage and Backup
Cloud data storage facilitates easily managing and backing up rapidly growing data volumes cost-effectively while making data accessible from anywhere.

Software Development
Cloud platforms provide efficient tools and infrastructure for developers to quickly build, test, and launch applications at scale.
Web Hosting
Using cloud infrastructure for web hosting is faster and more cost-effective than traditional web servers for launching online apps and websites.
File Sharing and Team Collaboration
Cloud-based file sharing and productivity suites empower teams to work together seamlessly online, increasing workforce mobility.
Key Considerations
While cloud computing delivers immense business value, some key factors to consider include:
Security and Compliance
Addressing security protections, access controls, and compliance with regulations is essential, especially when dealing with sensitive data.
Connectivity and Reliability
Minimizing network downtime that could disrupt cloud application availability is critical for certain workloads. Multi-cloud solutions spread risk.
Vendor Lock-In
Leveraging multiple IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS vendors avoids over-reliance on a single provider. This facilitates changing platforms if needed.
Conclusion
Migrating business functions to the cloud allows enterprises to reduce costs, drive innovation, collaborate better, and deliver superior customer experiences. Leading organizations are adopting cloud services for most IT needs.
With careful planning around security, connectivity, and vendor diversity, cloud computing delivers immense strategic and economic benefits.
FAQs
What are the main types of cloud computing?
The three cloud computing types: Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. IaaS provides fundamental computing infrastructure, PaaS offers a development and deployment platform, and SaaS allows cloud-based access to software applications.
What are some key benefits of the cloud for business?
Main business benefits include reduced costs, easy scalability, increased workforce mobility and productivity, faster innovation through rapid experimentation, and enhanced collaboration across teams and units.
Is the cloud secure for business data?
Leading cloud providers offer best-in-class security tools and practices stronger than most individual companies can achieve alone. However, businesses must enable security capabilities, access controls, and compliance processes when moving to the cloud.
How does cloud computing enhance customer experience?
The scalability and innovative capabilities of cloud platforms allow businesses to quickly build, test, and launch feature-rich web and mobile applications to understand customers better and deliver superior experiences.
How can businesses avoid vendor lock-in with the cloud?
Adopting multi-cloud solutions using different IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS vendors based on each business workload prevents over-reliance on a single cloud provider. This facilitates changing platforms smoothly if needed.