A network is a set of devices connected through links. It allows devices to communicate, share resources, and exchange information. Devices on a network can include computers, printers, servers, phones, access points, routers, switches, and more. The links connecting them could be physical cables or wireless technologies like WiFi.
Network Technology makes it possible for devices to communicate efficiently without having to be physically connected. They form the basis for sharing data and applications among distributed devices.
Table of Contents
Types of Networks
Several types of computer networks differ in their size and scope:
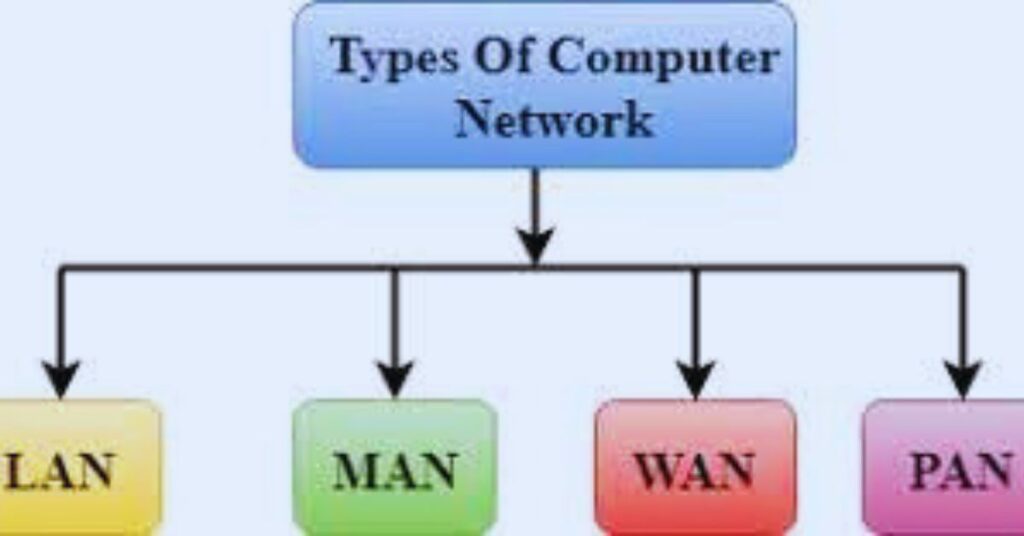
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN connects devices within a limited geographical area like a home, office building, or school. LANs enable devices to share resources like storage, printers, games, or applications.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN connects devices located in geographically separate areas like different cities or countries. The internet is the best example of a WAN.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
A MAN connects devices within a metropolitan area or city. It can connect some local area networks located in different buildings or campuses.
Personal Area Network (PAN)
A PAN allows devices on a person’s body to communicate with each other. Examples include connecting a smartphone to a wireless headset via Bluetooth.
Campus Area Network (CAN)
A CAN connects devices across a college or university campus. It can connect multiple LANs from different buildings and hostels.
Components of a Network
There are several key components required to build a functioning network:
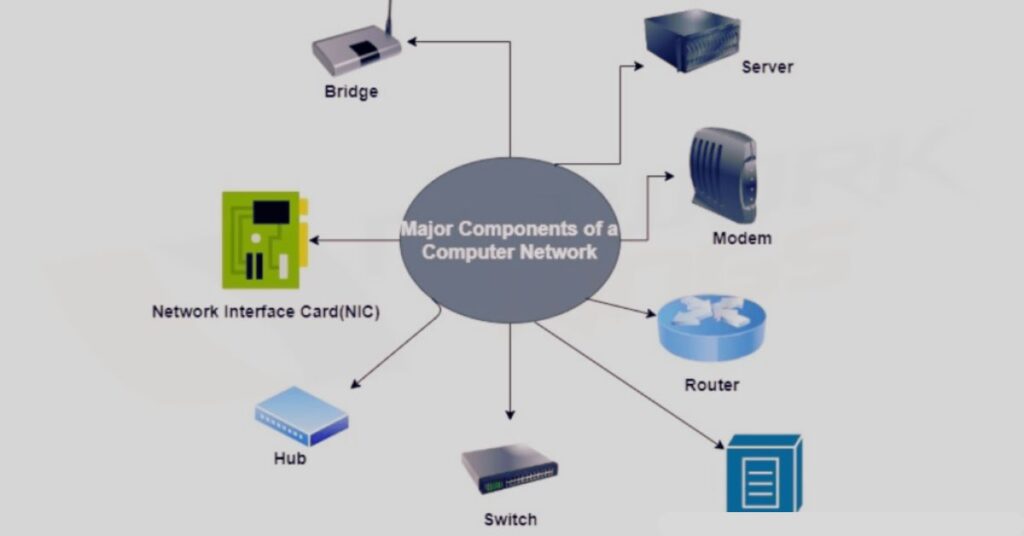
Servers
Servers are computers that store data, apps, and network services. They provide tools, resources, and services to client devices on the network. Examples are file servers, print servers, email servers, etc.
Connecting Devices
Network devices like routers, switches, and hubs connect computers and other devices on a network:

Routers
Routers connect networks to exchange data between them. They route packets to the appropriate destination network.
Switches
Switches connect devices within a network. They filter and forward data to the intended device destination.
Hubs
A hub broadcasts all network data to every port. Unlike a switch, it does not identify the intended destination.
Transmission Medium
The transmission medium carries network signals across links:
Wired Medium
This includes ethernet cables, fiber optic cables, coaxial cables, and telephone lines.
Wireless Medium
This includes WiFi, cellular data networks, microwaves, and satellites.
Network Topologies
Network topology refers to the physical layout of connections between devices. Common topologies include:
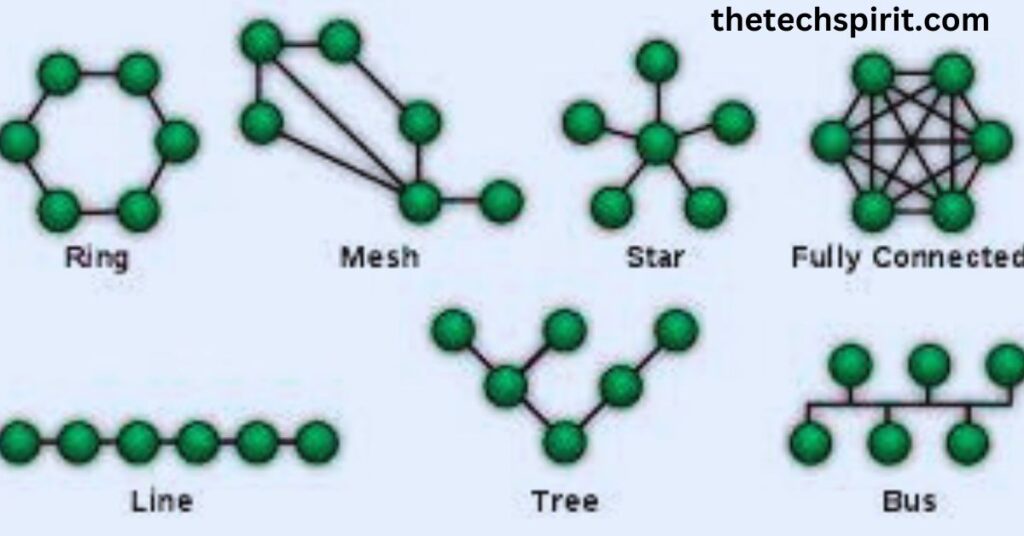
Star Topology
In a star topology, nodes connect to a central hub or switch. Data flows from the nodes to the central device before being forwarded to the destination node.
Bus Topology
In a bus topology, all devices connect to a main cable called the bus or backbone. Data transmitted by any device travels along the bus and can reach all other devices.
Ring Topology
In a ring topology, each node connects to exactly two other nodes forming a circular ring. Data travels around the ring from one node to the next until it reaches the destination.
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, each device connects to multiple other devices. This high degree of interconnectivity provides multiple paths for data communication.
Network Architecture
There are two primary network architectures:
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
In a P2P network, devices connect directly to each other for sharing resources like files or printers. There is no central server.
Client-Server
In a client-server network, client devices request resources or services from centralized servers. Servers provide and manage access to the apps, files, printers, etc.
Network Protocols
Protocols define rules for communication between network devices:
TCP/IP
The TCP/IP suite of protocols enables communication over the internet and most modern networks. TCP handles assembling data packets while IP handles addressing and routing.
HTTP
HTTP is the protocol used for transferring hypertext webpages over the internet. Web browsers and servers use HTTP to communicate and transfer data.
FTP
FTP enables transferring files between network devices. It provides access to files and sharing of software over TCP networks like the internet.
SMTP
SMTP is the protocol for sending emails across the internet. It defines how email servers exchange messages with each other using commands.
Network Security
Maintaining the security of network data and devices is crucial:
Firewalls
Firewalls monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and block unauthorized access. This prevents malicious threats from outside the network.
VPN
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) extends a private network over public networks to provide secure remote access. Data is encrypted for privacy.
Encryption
Encryption protects network communication and stored data by converting it into unreadable code. Only authorized parties can decrypt it.
New Trends in Network Technology
Some emerging trends shaping the future of networks include:
5G Networks
5G delivers ultra-high speeds, very low latency, and massive capacity compared to 4G. It will enable new applications requiring fast and reliable connectivity.
SDN (Software Defined Networking)
SDN enables dynamic configuring and managing network behavior through software. This makes networks fast, flexible, and scalable.
Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
NFV aims to virtualize network functions like routing and load balancing that were traditionally carried out by proprietary hardware.
IoT (Internet of Things)
The IoT consists of interrelated devices with embedded sensors, software, and connectivity enabling automated data exchange.
Conclusion
Network technology has evolved from simple file sharing to enabling today’s complex cloud computing systems and global communication via the internet. Advances like 5G, SDN, and NFV will further revolutionize how networks are built and managed.
As the number of devices connected to networks grows exponentially, network infrastructure needs to keep pace by becoming faster, more secure, and highly scalable.
Networking forms a crucial backbone that supports business, education, transportation, healthcare, defense, and society as a whole.
FAQs
What are the key benefits of a network?
Some benefits include sharing data and resources, central storage, communication between devices, remote access to information, and collaborative working.
What factors affect network performance?
Bandwidth, latency, error rates, and throughput impact network performance. Choosing the right topology and network architecture also improves speed and reliability.
How is a WAN different from a LAN?
WANs connect geographically distant areas while LANs are limited to small physical areas like a building. WANs use dedicated connections while LANs mostly operate over shared local connections.
What are network protocols?
Protocols are rules that allow efficient communication over networks. They define how data should be transmitted, routed, controlled, and received between network points.
Why is network security important?
Network security protects confidential data, personal information, and proprietary business data from theft and misuse. It safeguards the network from viruses and malware.









