Table of Contents
Introduction to Computer Networks
A computer network is a set of devices, nodes, and communication channels connected in a way that enables digital data transmission between endpoints. Essentially, a computer network facilitates resource sharing and information exchange between computers, servers, printers, and more. Networks are the foundation for delivering crucial computer networking services in the modern era.
Computer networks come in all shapes and sizes. Some span just a small area like a home or office, while others stretch between cities, countries, or the entire globe! The main network classifications include:
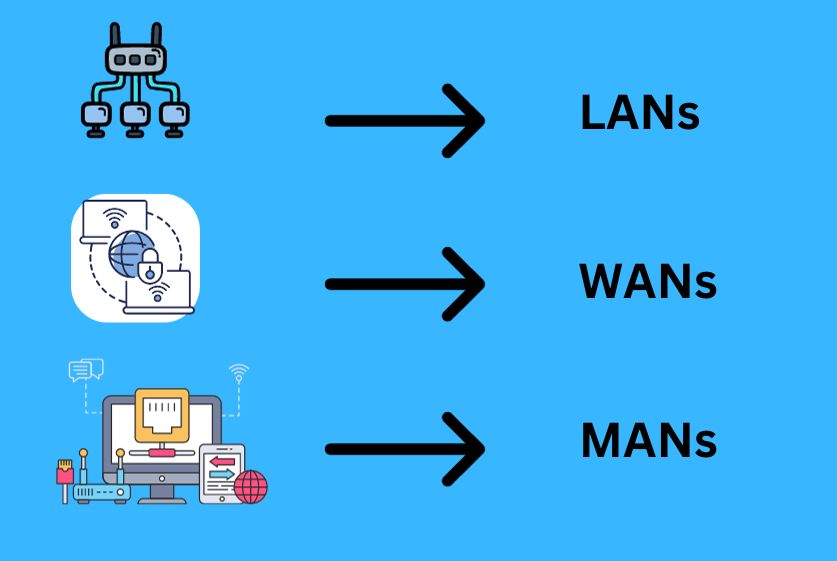
LANs
A local area network (LAN) connects devices over a relatively small geographic area, like inside an office building, school, or even someone’s home. LANs enable users to share resources like storage, printers, an internet connection, software applications, and more. The most popular LAN protocol is the Ethernet.
WANs
A wide area network (WAN) covers a larger physical range, connecting LANs across metropolitan, regional, national, or even international boundaries. The internet is the best example of a public WAN. Organizations also build private WANs to connect remote offices back to a corporate network.
MANs
A metropolitan area network (MAN) falls between LAN and WAN in terms of coverage range. MANs usually span multiple buildings or campuses over the area of a city.
For any network type, the components include network nodes (devices), communication media (wiring or wireless links), and network equipment. Nodes could be PCs, servers, printers, phones, security cameras, and more. They connect via cables, telephone lines, cellular links, satellite links, or other media. Networking gear like routers, switches, firewalls, and controllers tie everything together while regulating data flow.
Common Computer Networking Services
Network services are specialized applications hosted on servers to provide features or resources to clients over a network. They enable users to access files, share hardware assets like printers, manage identities and permissions, and more.
Here are some vital network services for the modern age:
File Sharing Services
File servers give users a central place to store files so anyone on the network can access them. This enables collaboration by having data in one repository versus scattered across individual devices.
Popular file-sharing protocols include:

Samba
Samba is a free software implementation for Windows interoperability. It allows UNIX-style systems like Linux and macOS to share files and printers with Windows PCs.
NFS
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol developed by Sun Microsystems allowing a server to share directories and files with clients over a network. It provides fast performance but lacks strong security mechanisms.
Printing Services
Print servers facilitate printer sharing across a network. This prevents the need to have printers at every desktop system.
CUPS
The Common UNIX Printing System (CUPS) provides printer drivers and management tools for UNIX-style operating systems. As an open standard, manufacturers can develop cross-platform drivers.
LPD
The Line Printer Daemon (LPD) is a network printing protocol that originated on BSD UNIX and became a standard on TCP/IP networks. It allows clients to submit print jobs to queues on TCP ports.
Directory Services
Directory services provide a centralized directory or database for managing user accounts, credentials, permissions, policies, and other objects. This allows administrators to set up access control and apply security measures.
LDAP
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) enables querying and modifying directory services running over TCP/IP. LDAP uses a relatively simple and efficient protocol.
Active Directory
Microsoft Active Directory is a directory service integrated with Windows domains to manage Windows environments. It handles authentication, authorization, and auditing using Kerberos and LDAP protocols.
Deploying Network Services
When it comes to rolling out networking services, proper planning goes a long way. But you also need to carefully implement and actively manage services after the initial installation.

Planning Considerations
Assessing user needs and evaluating security implications should happen early on:
User Needs
- Survey user workloads and access requirements
- Gather performance expectations
- Determine necessary integration with existing infrastructure
Security
- Classify sensitivity levels on accessed data
- Analyze regulatory compliance demands
- Audit for exposure threats from services
Implementation Steps
Once you select networking services to deploy based on plans, follow these implementation phases:

Install Server Software
- Acquire necessary server licenses
- Provision hardware (or virtual machines)
- Install server OS like Windows or Linux
- Enable core network protocols as needed
Configure Services
- Run service setup wizards
- Activate supporting services like DNS, DHCP IPsec
- Enter organization or domain info
- Create administrative accounts
Test Functionality
- Validate client connectivity
- Authenticate with user accounts
- Read/write files on shares
- Submit test print jobs
- Stress test with increased load
Ongoing Management
Daily responsibilities to keep services humming include:
Monitoring
- Watch for errors in log files
- Set performance alert thresholds
- Collect usage metrics for capacity planning
Backup
- Execute regular backup jobs
- Validate the ability to restore
- Retain offsite copies for recovery
Updates
- Obtain vendor security patches
- Test patches before deployment
- Schedule updates during maintenance windows
Troubleshooting Network Services
Despite the most careful plans and preparation, networking services can still fail. Troubleshooting the root causes takes detective work.

Diagnosing Connectivity Issues
- Verify cabling works properly
- Check DHCP scopes have available leases
- Test DNS resolution to service hostnames
- Confirm firewalls allow traffic on key ports
Fixing File Access Problems
- Validate user has permission to target share
- Check for lockouts from excessive login attempts
- Reboot the server or reset the networking service
Debugging Printing Failures
- Ensure the printer driver is installed
- Confirm print queue is started
- Check no jams or errors on the printer
- Verify connectivity over ports
The Future of Network Services
Technology keeps evolving, so the networking services of tomorrow will leverage cutting-edge developments:

Further Virtualization
Hypervisors and containers minimize hardware dependencies. Network functions morph into agile software apps.
Increased Automation
AI and machine learning handle monitoring, provisioning, maintenance, optimizations, and repairs.
Greater Adoption of the Cloud
Services shift from private data centers to multi-tenant public clouds for elastic scale and global reach.
Conclusion
Computer Networking Services make crucial functionality like file and print sharing available over a network. Directory services add identity and access management.
Careful planning when first deploying services gives way to attentive monitoring and maintenance to keep operations running smoothly. Virtualization, automation, and the cloud promise to transform networking services for the future by enhancing flexibility while reducing hands-on management.
FAQs
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory is Microsoft’s directory service for Windows environments. It centrally manages domain identities, permissions, policies, application settings, and other objects in a database to authorize access and enforce security.
How do I set up printer sharing?
Install printer-sharing software like CUPS on a Linux server or utilize Print Management on a Windows Server. Next, add network printers by making shared print queues. Finally, map printers to client systems based on the server name and shared queue.
What causes connectivity issues on a network?
Common culprits for connectivity problems include faulty network gear like NICs or switches, IP address conflicts, VPN disconnects, misconfigured firewall and security rules, DNS resolution failures, and using cables not suitable for the speed.
Is it secure to store files on a network share?
Using network shares to store files centralizes data for easier access but also introduces risks if proper precautions are not taken like setting share and NTFS permissions to authorize user access. Enable auditing to track activity. And consider encryption, multi-factor authentication, or other measures for sensitive shares.
What new developments are coming for network services?
Emerging trends around network services include increased use of virtualization and containers to abstract services from hardware, greater automation through artificial intelligence, and a shift from private data centers to multi-tenant public clouds. These improve flexibility and scalability.