The use of Cloud Technologies Solutions has become ubiquitous in recent years, with businesses of all sizes adopting these technologies. Cloud solutions provide access to computing resources, databases, storage, and software applications over the internet.
Instead of purchasing, installing, and maintaining infrastructure and software on-premises, companies can leverage the economies of scale provided by cloud providers. Numerous benefits are driving the adoption of cloud solutions, which this article will explore in detail.
Table of Contents
Benefits of Cloud Technologies Solutions
Flexibility and Scalability
One of the key advantages of the cloud is flexibility and scalability. With cloud computing, it’s easy to adjust resource usage up and down to meet changing needs.
This eliminates the need to purchase and install expensive infrastructure and software that may go underutilized.

Companies only pay for the computing resources they use each month, providing greater cost efficiency. Cloud infrastructure can scale seamlessly to accommodate traffic spikes, seasonal fluctuations, and business growth.
Cost Savings
The pay-as-you-go pricing model of cloud computing leads to significant cost savings compared to on-premises solutions. Instead of large upfront capital investments in hardware and data centers, cloud usage is treated as an operating expense.
Unused resources don’t have to be continually powered and cooled. Maintenance, upgrades, and security are handled by the cloud provider. Companies can avoid wasted IT infrastructure spending and reallocate those budget dollars.
Increased Collaboration
Storing data and applications in the cloud facilitates increased collaboration across teams and locations. Cloud-based workflows streamline cross-functional work.
Files stored in cloud drives can be accessed securely by employees everywhere. Video conferencing and messaging through cloud apps connect distributed teams.
The cloud provides a central platform from which a distributed workforce can collaborate effectively.
Enhanced Security
Leading cloud providers implement state-of-the-art security tools and practices that exceed the capabilities of most organizations. Cloud infrastructure is protected by firewalls, intelligent threat detection, redundant servers, encrypted data transmission, and regular software updates.
Providers undergo rigorous third-party audits to verify security. With the cloud, businesses can be assured their data and applications are safe.
Types of Cloud Solutions
There are three primary cloud computing models companies can leverage:
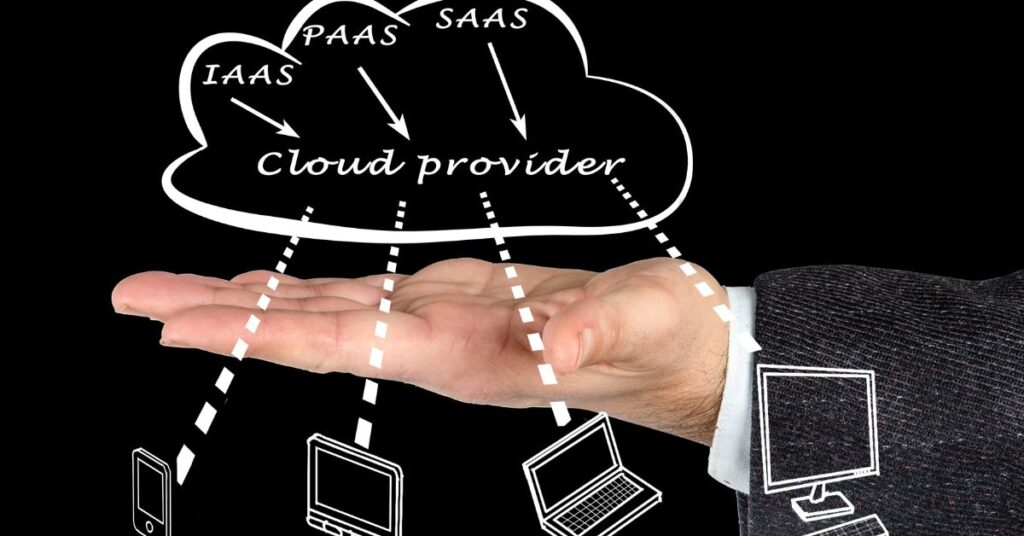
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
With Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), cloud providers offer pay-as-you-go access to fundamental computing resources including servers, storage, and networking.
Companies don’t have to purchase and manage their hardware infrastructure. Leading IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) delivers development tools, databases, and application management capabilities over the Internet.
Developers can quickly build, test, and deploy software without configuring underlying infrastructure. Salesforce’s Force.com and Heroku are popular PaaS options.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) provides web-based access to complete software applications. Common SaaS applications include email, conferencing tools, CRM, HR systems, and more. Companies pay a subscription fee to use the software.
The cloud provider handles all maintenance, support, and updates. Well-known SaaS products include Microsoft 365, Slack, and Salesforce.
Implementing Cloud Solutions
Transitioning business systems and data storage to the cloud requires careful planning and execution. Following best practices will ensure a smooth and successful deployment:
Assessing Needs
Thoroughly assess organizational needs, resources, workflows, and constraints.

Determine which systems are best suited for cloud hosting based on business requirements, compliance, and cost. A cloud readiness assessment yields insight into gaps needing remediation.
Moving Data and Applications
With needs defined, create a roadmap for migrating data and applications to the cloud. Take inventory of all systems and data. Calculate the required cloud capacity. Use tools provided by cloud vendors to facilitate smooth data transfer. Validate successful migration.
Training Employees
Any technology transition requires training employees on new systems and processes. Schedule onboarding sessions with ample time before launch. Ensure staff are comfortable accessing cloud apps and data. Publish user guides and FAQs. Be available to answer questions.
Ongoing Management
Manage the cloud environment on an ongoing basis just like on-premises systems. Monitor usage, performance, bandwidth, and costs. Ensure security protocols and access controls are configured properly. Keep software updated. Back up data regularly.
Cloud providers handle infrastructure maintenance and uptime.
Case Studies

Company A
Global retailer Company A was plagued by inflexible legacy IT systems. By transitioning core operations to AWS, Company A gained the ability to scale for sales surges.
Cloud data analysis enabled better inventory and supply chain optimization. Company A accelerated new store openings using cloud-based point-of-sale systems.
Company B
Engineering firm Company B struggled with slow software development cycles. By leveraging PaaS on Azure, developers now release updates multiple times daily versus quarterly. Company B gained real-time operational insights from cloud-based IoT analytics. Engineers collaborate globally on designs through cloud drives.
Conclusion
Cloud solutions deliver flexibility, cost savings, collaboration, and security. Leading platforms include IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Migrating wisely and managing ongoing operations ensures maximum value.
With the right strategy, the cloud can provide businesses with competitive advantages. As technology continues advancing, cloud adoption will only increase.
FAQs
What are the benefits of cloud solutions?
Cloud solutions offer flexibility, scalability, cost savings, collaboration, and enhanced security compared to on-premises infrastructure and software. Companies can quickly adjust usage and avoid wasted spending.
What are examples of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
Leading IaaS platforms include Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform. PaaS providers include Salesforce’s Force.com and Heroku. Popular SaaS applications are Microsoft 365, Slack, and Salesforce.
How do you migrate legacy systems to the cloud?
Assess needs, calculate required capacity, inventory data and applications, develop a roadmap, use cloud tools to transfer data, train employees on new systems, validate successful migration, and manage the cloud environment long-term.
Is the cloud secure?
Yes, leading cloud providers implement robust security tools and practices that typically exceed on-premises capabilities. Independent audits verify security. Encryption, firewalls, threat monitoring, and redundancy protect cloud data.
How can cloud solutions improve business performance?
The cloud provides access to advanced technology, frees budget for innovation, enables data insights, allows collaboration across distributed teams, and helps businesses quickly scale to meet changing demands.