Cloud Sourcing Definition refers to the practice of obtaining IT resources, infrastructure, platforms, software, and other technology services via the cloud rather than the traditional on-premises model. With cloud sourcing, businesses access technology services on demand from cloud providers via the internet.
In a nutshell, cloud sourcing allows organizations to tap into efficient, scalable, and flexible IT solutions without having to build and maintain them in-house. Instead of owning the infrastructure, hardware, or software, companies essentially rent them from cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform.
Compared to traditional IT outsourcing, cloud sourcing offers greater agility, faster deployment, lower upfront costs, and doesn’t lock you into lengthy contracts. It provides on-demand access to advanced technology while shifting the burden of maintenance, upgrades, and support to the cloud provider.
Table of Contents
Benefits of Cloud Sourcing Definition
Several key benefits make cloud sourcing an appealing option for many businesses today:

- Cost savings – No need to invest in expensive on-premises IT infrastructure and data centers. Pay only for the services used.
- Scalability – Quickly scale IT resources up or down to meet changing needs.
- Flexibility – Easily switch between services or providers. Avoid vendor lock-in.
- Agility – Rapidly test and deploy new platforms and applications.
- Business focus – Less time managing IT, more time on core competencies.
- Access to innovation – Leverage cutting-edge technology without big investments.
- Disaster recovery – Data backup and recovery built into cloud platforms.
- Collaboration – Cloud-based tools connect distributed teams and partners.
Cloud Sourcing vs. Outsourcing
While outsourcing and cloud sourcing both involve leveraging external providers for IT services, there are some key differences:
- Asset ownership – With outsourcing, assets are owned by the provider. Cloud sourcing is essentially “renting” IT resources.
- Cost structure – Outsourcing requires large upfront investments. Cloud sourcing is pay-as-you-go based on usage.
- Flexibility – Cloud sourcing allows switching between providers. Outsourcing has more vendor lock-in.
- Scalability – Cloud resources can scale on demand. Outsourcing requires renegotiating contracts.
- Skill focus – The cloud puts the focus on cloud skills vs. hardware/data centers.
- Strategic value – The cloud offers more opportunities for innovation and growth. Outsourcing is more tactical.
Types of Cloud Sourcing
There are three main types of cloud computing services that organizations can source:
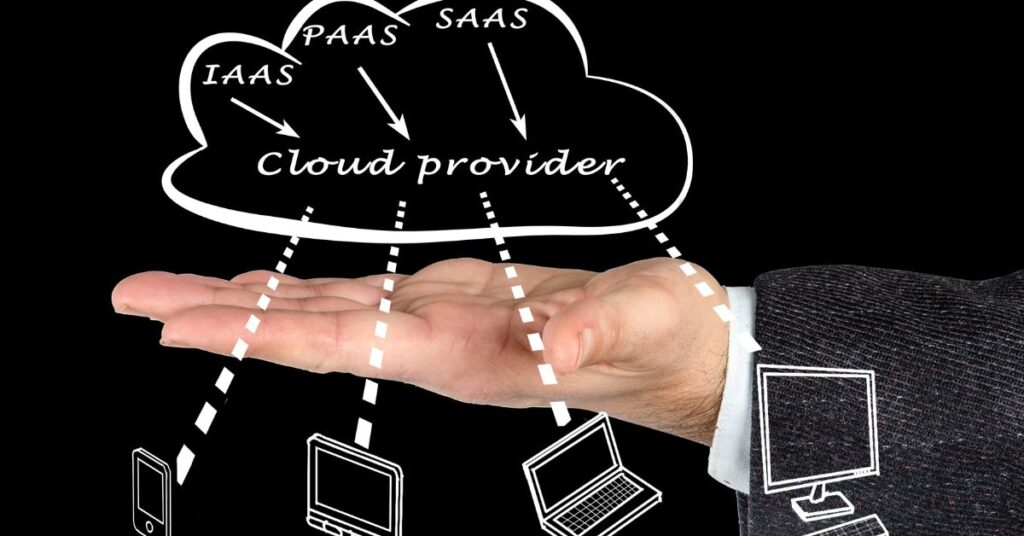
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The most basic level of cloud sourcing. With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure like servers, storage, and networking on an on-demand basis. Offers complete flexibility and requires no upfront investment.
Examples: AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a managed platform for building, testing, and deploying applications without maintaining the underlying infrastructure. Allows faster software development.
Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, Heroku.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
The most turnkey option. SaaS is essentially ready-to-use cloud-based software that is maintained, updated, and supported by the provider. Users access via a web browser.
Examples: Salesforce, Dropbox, Slack.
Cloud Sourcing Models
Cloud services are delivered via three fundamental models:

Public Cloud
Shared cloud resources are provided over the public internet by third-party providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP. Offers maximum flexibility and scalability.
Private Cloud
Cloud environment dedicated to a single organization, managed internally or by a third-party host. Heightened security and control but limited scalability.
Hybrid Cloud
Combines public and private clouds. Sensitive data remains private while shared services run in the public cloud. Provides the best of both worlds.
Risks of Cloud Sourcing
While cloud sourcing provides enormous advantages, potential risks include:
- Loss of direct control over IT systems and data
- Vendor lock-in and cost unpredictability
- Security and privacy concerns related to data transmission and storage
- Reliance on Internet connectivity for access
- Lack of customization options vs. in-house systems
- Integration challenges with on-premises IT environment
The Future of Cloud Sourcing
Looking ahead, we can expect cloud sourcing to become the default for IT services across industries. As cloud providers expand their offerings and address potential risks, the benefits will overwhelmingly outweigh any remaining barriers.
Machine learning, IoT, edge computing, and other emerging technologies will drive more organizations to adopt cloud sourcing. It enables leveraging these advanced capabilities without massive in-house investment.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also accelerated cloud adoption.
As remote work and digital engagement become the norm, cloud sourcing provides the flexibility and scalability needed to adapt quickly.
Conclusion
Cloud sourcing empowers organizations to tap into on-demand IT resources rather than maintaining them in-house. By leveraging public, private, or hybrid cloud platforms, businesses can deploy services faster and scale efficiently to drive innovation and growth.
While some risks remain, the profound benefits of agility, cost savings, resilience, and access to cutting-edge capabilities make cloud sourcing a pivotal long-term strategy across industries.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of cloud sourcing?
The main benefits are cost savings, scalability, flexibility, business agility, access to innovation, disaster recovery, and enabling collaboration.
Is cloud sourcing right for my small business?
Yes, cloud sourcing levels the playing field and lets small businesses access advanced IT capabilities on-demand that previously required major investments. It is ideal for startups and lean teams.
Is my data secure with cloud sourcing?
Leading cloud providers offer state-of-the-art security in transit and at rest. However, organizations must take steps to control access and implement sound cyber practices.
Does cloud lock me into vendors long-term?
Not necessarily. Avoiding vendor lock-in is easier with cloud sourcing than traditional outsourcing. But some due diligence is required.
How does cloud sourcing impact my IT team?
It typically shifts focus from infrastructure maintenance to developing value-added cloud solutions. Some roles may change but demand for cloud skills rises.









