Cloud Computing Experience has transformed the way organizations access computing resources and manage data. By utilizing on-demand services provided over the Internet, businesses can quickly scale resources up or down to meet changing needs without making large capital investments in hardware and infrastructure.
While the benefits of cloud computing are substantial, migrating legacy systems to the cloud can be daunting for IT teams and business leaders unfamiliar with cloud architectures. By understanding the fundamentals of cloud computing and following best practices, organizations can ensure a smooth and successful transition to the cloud.
Table of Contents
What is Cloud Computing and Why it Matters
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing resources over the internet. Rather than maintaining costly data centers, organizations can leverage the economies of scale provided by major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
The key advantages of cloud computing include:
- Cost savings – No need to purchase hardware or maintain facilities. Pay only for what you use.
- Scalability – Quickly scale resources up or down based on demand.
- Flexibility – Deploy resources as you need them. Use multiple cloud providers.
- Productivity – Reduce IT maintenance so staff can focus on innovation.
- Reliability – Leverage cloud provider expertise in security and resilience.
With the rise of remote work and digital transformation, cloud computing allows organizations to be agile and adaptable in a dynamic business environment.
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
While cloud computing provides substantial benefits, there are some potential drawbacks to consider:
Pros:
- Reduced costs and Capex spending
- Nearly unlimited scalability
- Business continuity and disaster recovery
- Access to the latest technology innovations
- Environmentally friendly
Cons:
- Loss of control and vendor lock-in risks
- Limited customization options
- Dependence on Internet connectivity
- Multi-cloud complexity
- Security and compliance concerns
The pros tend to outweigh the cons for most organizations. Risks can be mitigated through careful planning, governance, and working with trusted cloud providers.
Types of Cloud Computing Experience Services
There are three main types of cloud computing services:
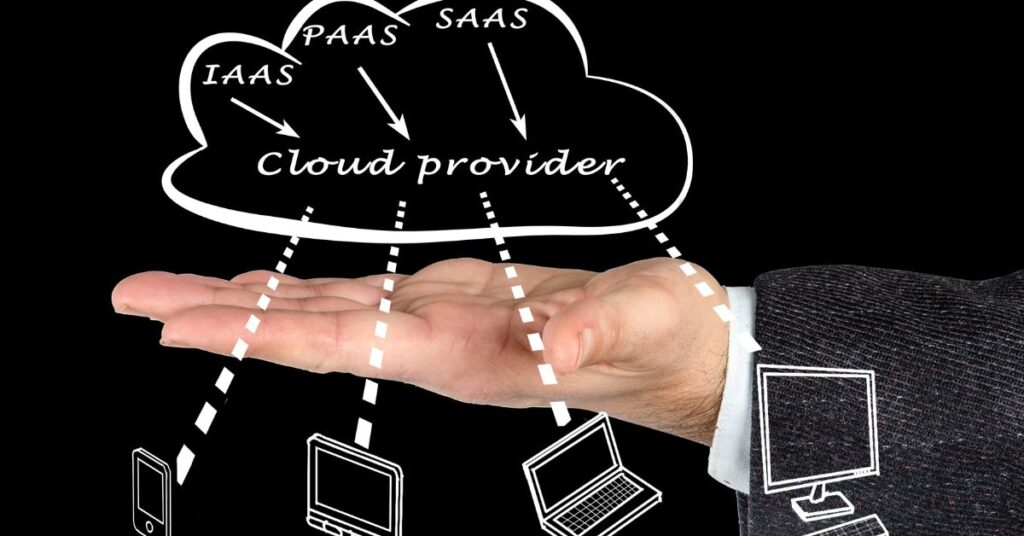
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) – Provides access to fundamental computing resources like servers, storage, and networking. Examples: AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) – Managed cloud environment for developing, testing, and deploying applications. Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service
- Software as a Service (SaaS) – Cloud-based applications accessible via a web browser. Examples: Office 365, Salesforce, G Suite
Organizations combine these services in a cloud architecture to meet business needs.
Getting Started with Cloud Computing
Migrating legacy systems to the cloud takes careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices:
- Assess workloads – Inventory systems and data. Analyze usage trends.
- Select cloud provider(s) – Compare offerings from AWS, Azure, GCP, and others.
- Design cloud architecture – Map out infrastructure, services, and security controls.
- Migrate apps/data – Lift-and-shift vs. rearchitecting approaches.
- Validate functionality – Test systems thoroughly after migration.
- Manage/optimize – Monitor usage, automate processes, and adjust resources.
Consulting with cloud experts is highly recommended to create an effective cloud adoption roadmap.
Key Steps for Moving to the Cloud
Migrating to the cloud follows a general sequence of steps:

Pre-migration
- Assess readiness
- Select initial workloads
- Choose cloud provider(s)
- Design new architecture
- Test migration process
Migration
- Migrate apps and data
- Validate successful migration
- Optimize architecture
Post-migration
- Manage cloud environment
- Migrate additional workloads
- Drive cloud-native development
- Continuous optimization
Following a phased approach allows organizations to minimize risks and build internal capabilities.
Best Practices for Cloud Security
As with any IT environment, cloud security should be a top priority. Strategies include:
- Manage identities and access carefully
- Implement the shared responsibility model
- Encrypt sensitive cloud data
- Use cloud-native security tools
- Automate security monitoring and response
- Maintain strong network security
- Regularly review security configurations
- Conduct penetration testing
- Back up data and systems
Working closely with cloud providers on security is key to reducing risks.
Top Cloud Computing Providers
Leading cloud platforms include:
- Amazon Web Services – the most widely adopted IaaS provider
- Microsoft Azure – strong hybrid cloud options
- Google Cloud Platform – expertise in analytics and machine learning
- IBM Cloud – focus on emerging technologies like AI
- Alibaba Cloud – major presence in Asian markets
The top players provide a wide array of services on a global scale. Factors like industry focus can help guide provider selection.
Use Cases and Examples
Cloud computing is leveraged across industries for key use cases:
- Application modernization – Re-architect legacy apps using cloud-native tools.
- Disaster recovery – Replicate systems to the cloud for availability.
- Big data analytics – Perform analysis on vast data sets using cloud data platforms.
- Software development – Build and deploy modern apps faster.
- Internet of Things – Ingest and process huge data volumes from connected devices.
- Mobile apps – Deliver rich mobile experiences by integrating cloud backend services.
The Future of Cloud Computing
Analysts expect strong growth as more workloads migrate to the cloud:
- Hybrid and multi-cloud adoption will accelerate
- Cloud-native development practices will expand
- Serverless computing will gain adoption
- Cloud-based AI will become mainstream
- Edge computing will complement cloud data centers
As capabilities grow, virtually every organization will leverage cloud services in some form within 5 years.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Migrating systems, data, and processes to the cloud can enable greater business agility and efficiency. However, cloud adoption requires careful planning and execution.
With the right strategy, organizations can smoothly transition to cloud-based models and maximize benefits over the long term.
Key points:
- Assess workloads and select cloud providers carefully based on needs.
- Design cloud-based architectures for scalability, resilience, and security.
- Validate system functionality after migration and optimize continually.
- Leverage cloud provider expertise in operations, security, and innovation.
- Adopt cloud-native approaches to fully realize the advantages.
By following proven best practices, IT teams can ensure their organizations have a positive cloud computing experience.
FAQs
What are the main benefits of cloud computing?
The main benefits include cost savings, scalability, business continuity, accessing the latest technology, and increased productivity/efficiency.
Is transferring data to the cloud secure?
Cloud providers offer robust security tools and practices. However, organizations must take responsibility for properly configuring and managing security based on the sensitivity of data.
How quickly can cloud resources be provisioned?
A key advantage of the cloud is near real-time provisioning of compute resources, storage, and other services on-demand to meet spikes in usage.
What migration strategies are used for legacy systems?
Common approaches are lift-and-shift migrations or rearchitecting applications using cloud-native technologies. Organizations can combine these strategies.
How are costs managed in the cloud?
Cloud providers offer advanced tools for monitoring usage and controlling costs. Best practices include optimizing resource usage, automating the shutdown of idle resources, and utilizing cost-effective services.









