Cloud computing activity refers to the delivery of computing services like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the Internet (“the cloud”).
Resources are provided quickly and easily via the cloud without direct active management by the user. Cloud computing provides access to information as services whenever and wherever users need it.
Table of Contents
Benefits of Cloud Computing Activity
Cloud computing offers organizations many benefits:
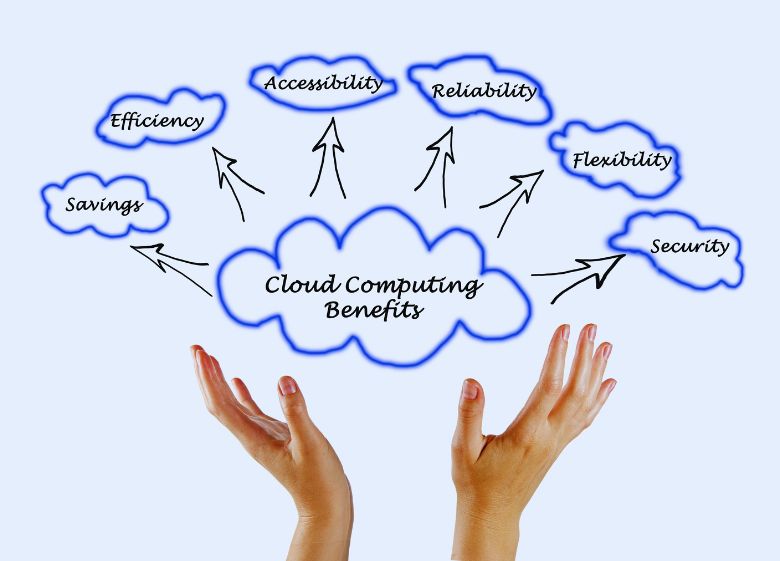
Cost Savings
Cloud computing eliminates the high costs of purchasing and maintaining your own computing infrastructure. It converts fixed costs into variable costs as you only pay for the resources you use.
Scalability
Resources can be rapidly provisioned to match demand. You can scale services up or down to meet spikes or dips in traffic. This makes the cloud ideal for variability and growth.
Mobility
Employees can access data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. This enables a mobile workforce.
Increased Collaboration
With data stored centrally online, teams and employees can better collaborate on projects and documents.
Flexibility
Cloud computing provides more flexibility in deploying and accessing assets. Resources can be deployed globally to provide better redundancy.
Security
Leading cloud providers offer robust security tools and practices. The scale of cloud providers also enables higher levels of security than most organizations can achieve alone.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are three main types of cloud computing:
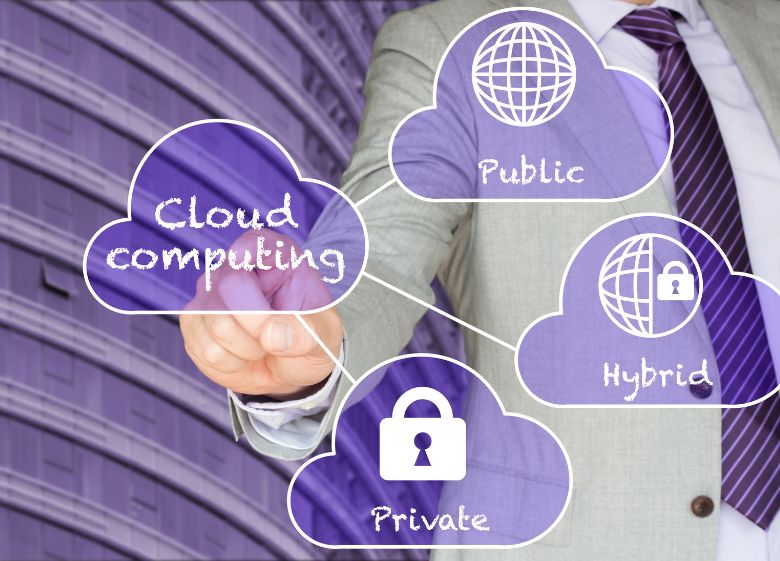
Public Cloud
Public cloud services are offered via the Internet and available to anyone. Resources are shared between different organizations.
Private Cloud
Private cloud services are delivered via a private IT infrastructure for a single organization. Resources are used exclusively by one customer.
Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds. Sensitive assets are maintained privately while shared services run in the public cloud.
Cloud Computing Models
Cloud computing provides services based on three models:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS offers access to fundamental computing resources like servers, storage, and networking. Users deploy software as needed.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides a platform with pre-built components to develop, run, and manage applications without maintaining infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS allows users to access cloud-based applications. The provider hosts both the application and infrastructure.
Major Cloud Providers
Some of the top cloud computing providers include:
Amazon Web Services
The most popular IaaS provider, offering a vast array of infrastructure and other cloud services.
Microsoft Azure
A rapidly growing provider of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, competing closely with AWS.
Google Cloud
Provides IaaS, PaaS, SaaS focused on big data, machine learning, and security.
IBM Cloud
An enterprise-focused provider of hybrid cloud computing services.
Alibaba Cloud
The leading Chinese provider of public cloud infrastructure and services.
Cloud Computing Use Cases
Popular uses of cloud computing:
Data Storage and Backup
The cloud offers affordable, unlimited data storage and backup capabilities.
Software Testing and Development
Cloud resources can be leveraged for continuous integration and testing environments.
Web Hosting
Websites, web apps, and blogs can be hosted in the cloud simply and cost-effectively.

Media Streaming
Media platforms use cloud computing for highly scalable media encoding and streaming.
Business Applications
Cloud-based SaaS replaces traditional on-premise software for HR, CRM, collaboration, and more.
The Future of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has seen rapid adoption, but still has ample room for growth – especially emerging technologies like server less computing, edge computing, and multi-cloud. As cloud services expand in scale, performance, sophistication, and addressability of specialized workloads, cloud adoption will continue marching forward. Security and compliance will remain top priorities.
Hybrid and multi-cloud will become the preferred approach for most organizations. The public cloud market is forecast to surpass $1 trillion by 2027. The future of enterprise IT is in the cloud.
Conclusion
In closing, cloud computing has fundamentally transformed business IT infrastructure by enabling on-demand access to computing resources over the Internet. The cloud provides organizations with increased efficiency, agility, mobility, scalability, and security while reducing costs. Leading public cloud providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google offer a vast range of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services.
As cloud services expand in sophistication, security, and hybrid integrations, enterprise adoption of cloud computing will continue to accelerate rapidly over the next decade.
FAQs
What are the benefits of cloud computing?
The main benefits of cloud computing include cost savings, scalability, increased mobility, flexibility, enhanced security, and greater collaboration capabilities.
What are the different types of cloud computing?
The three main types are public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Public cloud services are available via the Internet for public use. Private cloud services are used exclusively by a single organization. A hybrid cloud combines public and private cloud infrastructure.
What are some examples of cloud computing providers?
Major cloud computing providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, IBM Cloud, and Alibaba Cloud. AWS is currently the leading public IaaS provider.
What are the different cloud computing service models?
The three models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides fundamental computing resources, PaaS offers a development platform, and SaaS enables access to cloud-based applications.
What industries are adopting cloud computing services?
Cloud computing is being adopted across virtually every industry, including healthcare, life sciences, financial services, media and entertainment, manufacturing, retail, telecommunications, government, education, and more.









